WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AC AND DC WELDING?
Jan 05, 2024
Arc welding comes in two forms, AC and DC, utilizing distinct currents to create an electric arc. In both welding methods, an electric arc is established between an electrode and the metal undergoing welding, supplying the necessary heat for metal fusion. To generate this arc, a power supply is employed, which can either be based on alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). The decision between AC and DC as the power source determines the polarity of the electrical current coursing through the electrode. Moreover, the chosen power source significantly influences the resulting weld.
The strength and quality of your weld hinge on the proper selection of electrode polarity, commonly referred to as 'straight' or 'reverse.' These polarities are also known as 'electrode negative' and 'electrode positive.' Notably, DC polarity remains constant, while AC polarity follows a pattern of flowing in one direction for half of the time and then reversing direction for the other half.
DC Welding Explanation
DC welding is a type of welding that uses direct current to create an electrical arc between the welding electrode and the metal being welded. The electrical current flows in one direction, from the negative electrode to the positive metal workpiece. This creates a concentrated heat source that melts the metal and fuses it together.
AC Welding Explanation
AC welding is a type of welding that works by using an electrical current that alternates between flowing in one direction and then reversing direction many times per second. This alternate current generates an electric arc with fluctuating intensity between an electrode and the workpiece. The heat from the arc melts the metal, allowing it to be joined together.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| DC |
High quality Smoother Ideal for steel Greater penetration |
Prone to arc blow Difficult to control Expensive |
| AC |
Low cost Better for magnetic materials Effective on aluminium Efficiency |
Spatter Less smooth Less reliable |
| When to Weld with DC | When to Weld with AC |
| 1.You need the smoothest weld possible | 1.Weld appearance isn’t as important |
| 2.You can afford the welder you want | 2.You’re on a limited budget |
| 3.When welding thin metals | 3.You need deep penetration of plate metals |
| 4.You’re inexperienced at welding | 4.Welding metals with a magnetized field |
| 5.When doing overhead or vertical welding | 5.Whenever you’re welding aluminum |
All SSimder welding machines are DC welding machines, but this does not mean that we have not overcome the shortcomings of DC welding machines.
Hard to control? We have Synergic mode on SD-4050 Pro and Upgraded SD-4050Pro[2024]
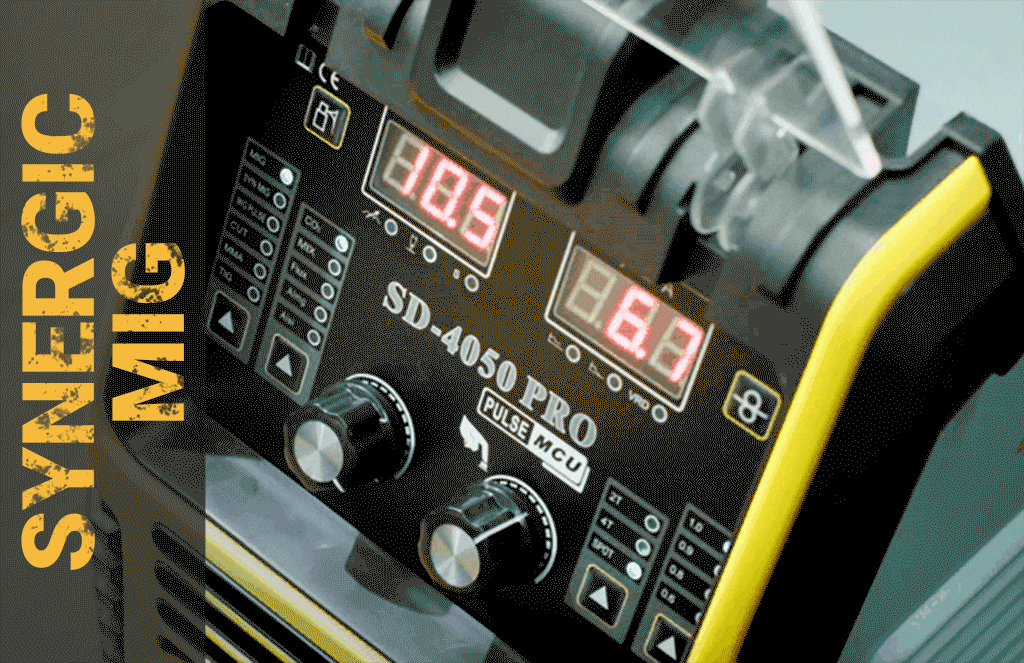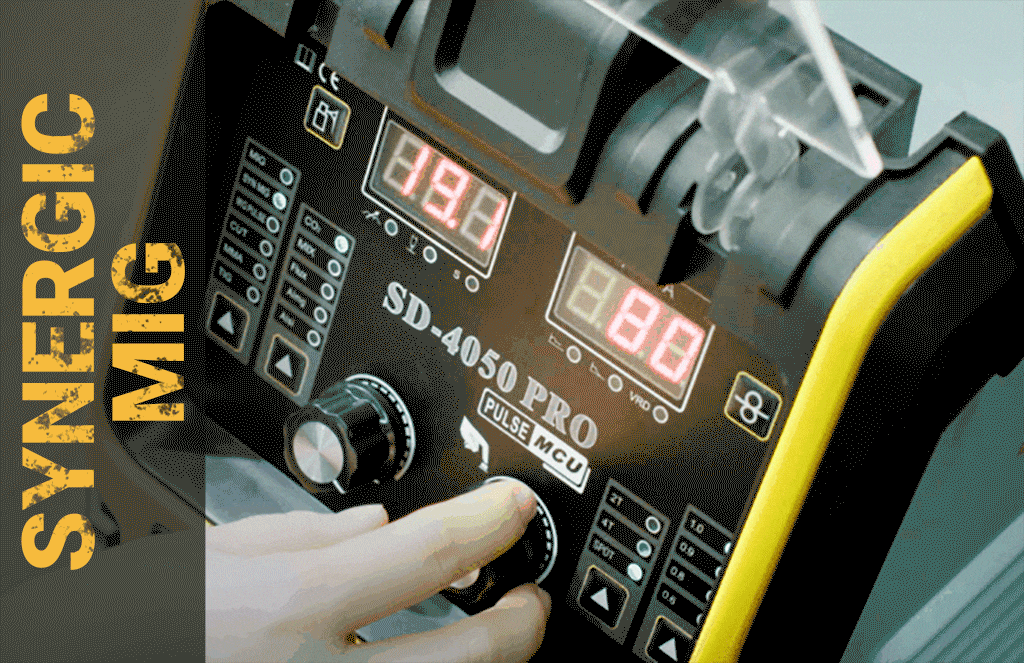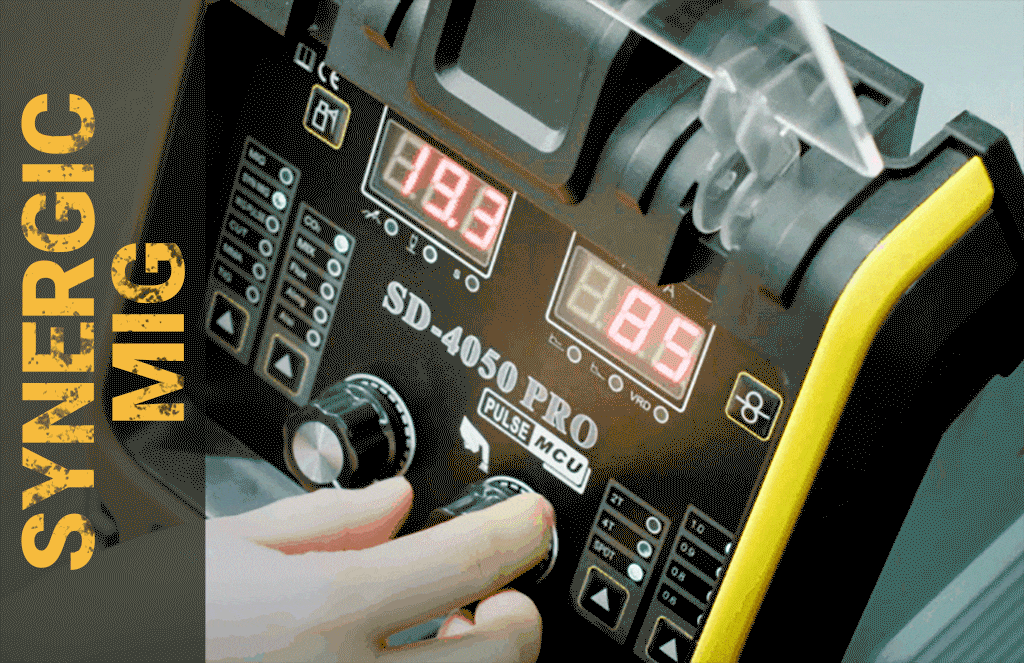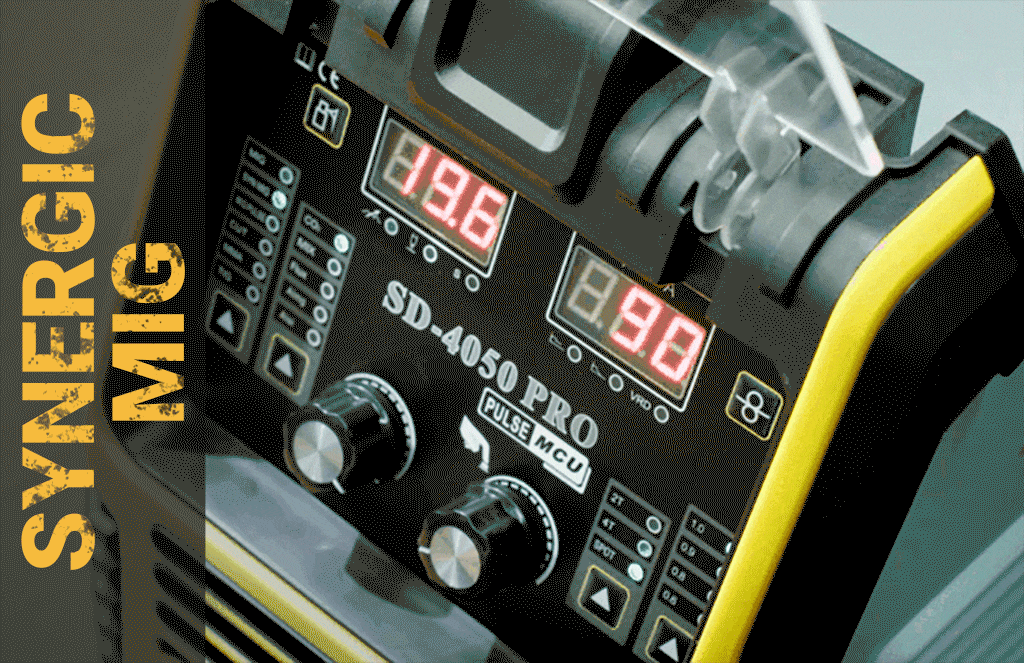
Expensive? We have small welding machines with a minimum price of less than 100 US dollars, which also have powerful performance. If you think our SD-4050PRO and 2024 upgrade models are expensive, you might as well learn more about how much convenience and powerful functions they can bring to you. Powerful The 10-in-1 welding machine supports foot pedals and spool guns. The memory function can store 10 different sets of welding parameters. It has passed the hellish environment assessment. Whether it is welding or cut, no matter what welding needs you have, just All you need is this welding machine.






Upgraded $999 $799SD-4050Pro[2024]
$999? $799!
Applications:
AC welding finds its application in scenarios where arc blow needs to be minimized, such as welding in the presence of magnetic fields or when working with materials prone to arc deflection.
DC welding is widely used across diverse applications, offering greater control and versatility. It is commonly employed in construction, fabrication, and pipeline welding due to its stability and precise control over the welding process.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the choice between AC and DC welding depends on various factors, including the specific welding application, material type, and desired welding characteristics. Understanding the fundamental differences between AC and DC welding is crucial for welders to make informed decisions that optimize efficiency and ensure high-quality welds in their projects.



